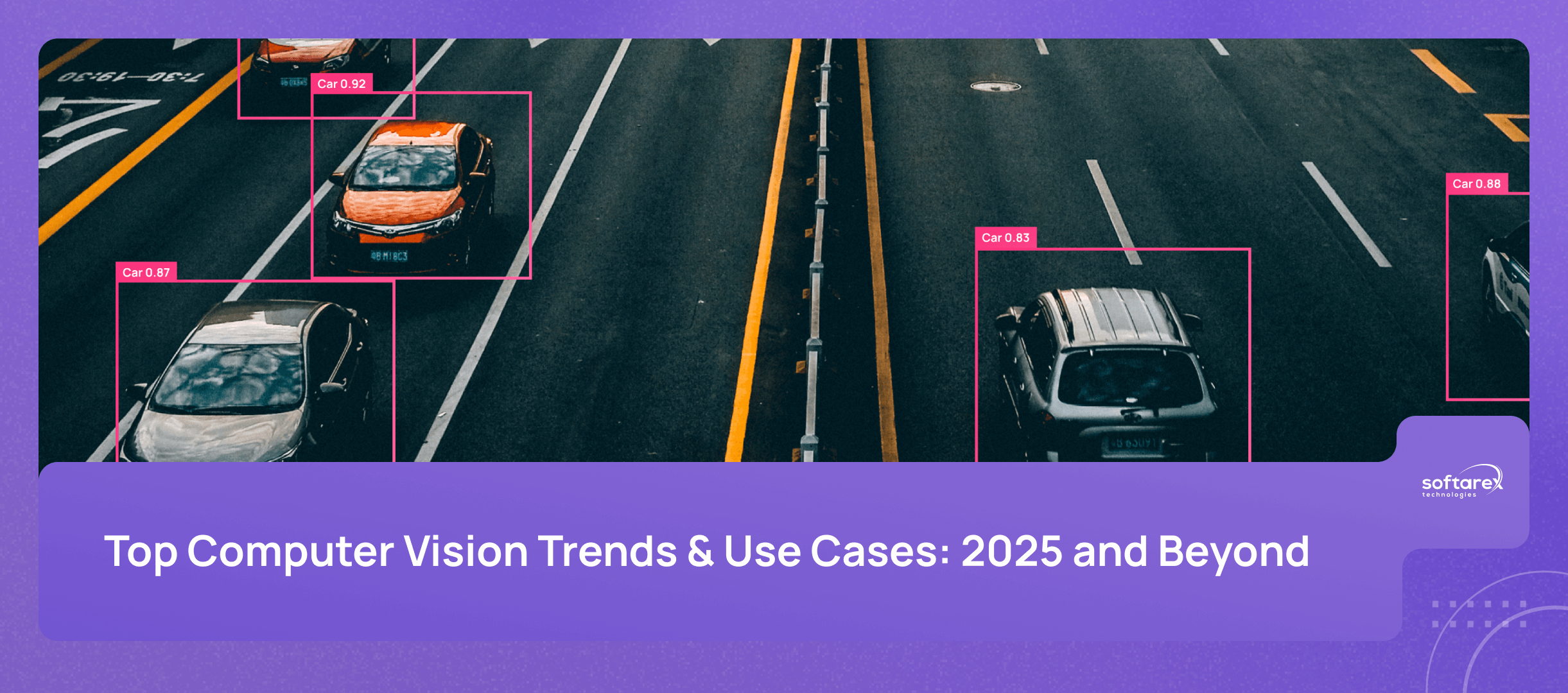
While generative AI and its fascinating applications have dominated headlines in 2024, another AI subset has been quietly driving innovation across industries around the world—computer vision. The global market for this technology is rapidly growing. Experts predict it will double in size and reach USD 45.7 billion by 2028.
The industry currently benefiting the most from computer vision is healthcare. Providers are leveraging the power of AI-driven diagnostic imaging to enhance accuracy, ensure safety, and improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, the impact of smart visual processing can be seen in retail. In this sector, businesses are implementing computer vision applications to automate inventory management and prevent shrinkage—a major financial problem of modern-day retailers.
Another exciting use case is autonomous vehicles, where the technology aids in navigation, obstacle detection, and safety. Self-driving cars are already being used in the taxi industry, making transportation safer and more sustainable.
And one more sector where computer vision has been making remarkable strides this year is drone-based disaster response. Equipped with advanced visual analysis capabilities, copters are aiding emergency teams in search-and-rescue missions and assessing the damage caused by natural calamities.
In this article, we are going to explore the hottest computer vision applications across these four industries and sneak a peek into the future to see what 2025 will bring.
Enabling Better Diagnostic Decisions
Imaging diagnostics is undoubtedly one of the areas of healthcare, where computer vision delivers the greatest value. 2024 has been a year of bright scientific and technological breakthroughs in the field of radiology.
For example, researchers at Microsoft, Providence Health System and the University of Washington developed BiomedParse, an AI model for holistic and more targeted medical image analysis. Trained on a dataset comprising 6 million of visual objects and texts, the new solution can accurately assess nine modalities, including CT scans, MRIs, X-ray images, and ultrasounds.
By relying on GPT-4, BiomedParse offers a less time and effort-consuming alternative to bounding boxes. Now, radiologists can specify what they are looking for in an image with a simple natural language prompt like “tumor” or “fracture”, and the model locates the abnormality with pixel-level precision.
Researchers claim the solution can identify tumors, melanoma, cystoid macular edema, COVID-19 chest infections, and brain glioma, among other conditions, outperforming its market rivals in accuracy.
While Microsoft’s solution is a research prototype that has a long journey ahead before reaching the market, one of the Nanox AI’s computer vision applications has recently received an FDA clearance. HealthCCSng V2.0, the upgraded version of the company’s medical imaging solution that has already proven effective in cardiac imaging.
Just like its predecessor, the new application is designed to aid in identifying patients at high risk of coronary disease. It measures coronary artery calcium (CAC)—a primary factor for future cardiovascular events—in routine, non-gated, non-contrast CT scans of patients aged 38-85.
The upgraded solution also adds new features to make cardiac imaging even more effective and accurate. For example, it includes a Zero CAC Category, which helps physicians distinguish between patients with zero and low CAC levels, where zero indicates a very low cardiovascular risk.
By offering a unified approach to cardiac imaging analysis, HealthCCSng V2.0 is bridging the gap between radiology and cardiology. The two medical specialties use different terms and descriptions to assess images, which often results in patients slipping through the cracks. The Nanox AI’ solution helps physicians avoid such incidents and make sure every patient gets directed to the preventative care they need, ultimately improving outcomes.
HealthCCSng V2.0 has received a Special Mention on TIME’s Best Inventions of 2024 list, an annual compilation of the 200 most impactful and innovative products, technologies, and ideas over the past year.
Tackling Inventory Gaps and Shrinkage
For retail, 2024 has been full of exciting computer vision applications across the industry’s landscape. Businesses continued reaping the benefits of smart visual solutions to improve poor inventory management. Statistics show that currently 58% of retailers struggle with less than 80% inventory accuracy, which means there’s a 20% chance that a product a customer wants is not in stock. This results in nearly $1 trillion in lost sales as businesses fail to meet consumer demand for products they don’t have available.
To address this challenge, Wakefern Food Corporation has expanded the adoption of its inventory-monitoring robots to 60 additional ShopRite locations. These smart assistants patrol store aisles, scanning shelves to ensure they are fully stocked, items are in the correct location, and the pricing is accurate. This automation allows human employees to stay focused on customer service, leaving the mundane, time-consuming work to the machines. Furthermore, with real-time alerts about inventory issues like low-stock or misplaced products, store teams ensure product availability and prevent customer churn.
Another critical issue computer vision applications have been helping retailers to tackle is shoplifting. 85% of participants in the Food Industry Association’s survey called it one of the most detrimental challenges affecting their performance. This year, the store theft rate has hit a record high indeed—the first half of 2024 has seen 24% more incidents than over the same period in 2023.
Experts believe the reason for this drastic surge is the increasing number of self-checkouts. While originally designed to cut wait lines and improve customer service, automated cash registers have unfortunately created new opportunities for shoplifting. Taking advantage of the lack of supervision, customers are increasingly treating themselves to “discounts” by simply not scanning items or scanning more expensive items as cheaper ones. The Design Against Crime Research Centre found that in the UK, far more carrots are recorded at self-checkouts than are actually purchased, which highlights the prevalence of the product-switching practice.
The theft problem is making retailers if not fully abandon the whole self-scanning shopping concept but rethink it. Walmart, for example, is introducing invisible barcodes, fully imperceptible to the human eye. Unlike traditional barcodes, these codes are printed all over the packaging, which makes it way easier for shoppers to register products without looking for the perfect angle. Self-checkout machines will get equipped with smart computer vision scanners capable of accurately identifying items even when customers are trying to hide them. This innovation is set not only to help prevent theft but also significantly speed up the shopping experience.
Modernizing Taxi Services with Autonomous Vehicles
Although self-driving vehicles are not yet a reality, it’s safe to say they’re far away from being science fiction either. Today, US drivers can experience a fully autonomous taxi ride with Waymo. The formerly known Google Self-Driving Car Project weekly provides over 100,000 trips to its app users. Drivereless taxis are available in three major US cities—Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Phoenix. Beginning in early 2025, the company is expanding its partnership with Uber and bringing the innovation to Austin and Atlanta customers.
The latest, sixth-generation Waymo cars, leverage the power of AI and computer vision to provide drivers with a 360-degree field view of the environment and the ability to identify objects up to 500 away, day and night, and in poor weather conditions.
When it comes to security, the most widely discussed concern regarding self-driving vehicles, the company has made it its top priority. For example, the proprietary Safe Exit feature reduces dooring events by detecting cyclists and passengers approaching the car and alerting the driver as they prepare to get out.
Statistics show the brand’s efforts to make self-driving safe and risk-free to be effective. Waymo researchers compared the amount of road incidents an average human has to the one the brand’s car does over the same 25-mile distance. The results proved Waymo safer than regular ones, with 34 fewer airbag deployment crashes, 67 fewer injury-causing crashes, and 81 fewer police-reported crashes.
While Waymo is setting the standard for practical deployment of self-driving cars, academic research worldwide is paving the way for future innovations. This year, a paper from Tsinghua University in China introduced a breakthrough advancement in computer vision that shows great promise to improve autonomous vehicle performance. Inspired by the human visual system, researchers designed a chip capable of sensing and processing 10,000 frames per second. This incredible perception speed could enhance the real-time object detection and navigation capabilities for autonomous vehicles, making driverless cars even safer and more efficient.
Ensuring Proactive Disaster Response
Today, computer vision-enabled drones are an indispensable assistant for humanitarian teams during natural disasters. By providing real-time situational awareness, precise mapping, and rapid damage assessment, the technology enables faster, more informed decisions in critical situations.
However, the market lacks solutions designed with search and rescue operations in mind. Often, emergency services use surveillance and payload drones that don’t have the capabilities needed for effective disaster response, delaying the delivery of necessary aid to people in danger. This is prompting researchers to further explore the capabilities of intelligent drone imagery.
One example of such R&D efforts is a project by students at the MIT World Peace University in India. They have recently developed an AI and computer vision-powered system that employs a multicopter to detect people in inaccessible areas, provide actionable insights on damage to S&R teams, and enable precise delivery of food and medicine to victims. According to the researchers, the solution aims to accelerate the speed, accuracy and effectiveness of disaster mitigation activities, ultimately reducing human suffering and saving lives.
Another aerial technology breakthrough in the field of natural disaster response is a project by Dr. Robin Murphy, Texas A&M University professor and founder of disaster robotics, and her research team. They spent over a year creating the world’s biggest open-source set of disaster damage imagery. Known as CRASAR-U-DROIDS, the repository includes photos taken via drone from 10 major calamities, including Hurricanes Harvey, Michael, Ida, Laura, Ian, and Idalia. The team engaged 130 high school students from Texas and Pennsylvania to label the level of damage caused to 21,700 buildings on 16,500 acres of land and 400 miles of roads.
They used this data to train computer vision algorithms to recognize damage caused by disasters to buildings and roads in images of affected areas. With this system, emergency response teams can remotely assess the level of destruction in just four minutes just by using a laptop. According to researchers, this provides immense value to countries that don’t have the resources to perform physical damage evaluations but do have inexpensive drones. The new system has already been used to determine the extent of infrastructure harm caused by Hurricanes Debby and Helene.
What 2025 Has in Stock for Computer Vision
As we reflect on 2024, we can see computer vision evolving and moving decisively from theoretical potential to practical applications across industries. Healthcare has seen the most dramatic transformation this year, with AI-powered diagnostics advancing from experimental prototypes to FDA-approved solutions. This is a clear signal that these technologies will soon become a standard component of medical practice, fundamentally changing how diseases are detected and treated.
In the commercial sector, computer vision applications have been delivering measurable returns. Retailers are successfully deploying smart automation to combat inventory challenges and losses, while the taxi industry’s growing investment in autonomous technology demonstrates that self-driving vehicles are no longer a distant dream but a rapidly advancing reality.
Perhaps most impressively, computer vision has proven its worth in life-critical applications. The successful deployment of AI-powered drones in disaster recovery operations shows that this technology has matured into an essential tool for tackling real-world challenges.
Looking ahead to 2025, the momentum continues to build. As algorithms improve, datasets expand, and new hardware capabilities emerge, even more sophisticated computer vision applications are expected. The rapid pace of adoption across industries makes it clear that this is not just a trend, but a critical technology shaping the future of business operations, innovation, and problem-solving.
At Softarex, we’re at the forefront of helping businesses leverage this transformative technology. By developing custom computer vision applications, we help organizations tackle their most pressing challenges, drive innovation, and unlock real value. If your business is ready to capitalize on the potential of computer vision, reach out to us today to explore how we can help bring your next project to life and drive measurable results.
If you’re interested in finding out more about how much it costs to get started and what you can expect in terms of return on investment, have a look at our Computer Vision Price Guide Every Business Needs. You can also download a free Project Kickoff Checklist to help you plan and structure your next initiative.