In this article, we break down the computer vision trends of 2025 and the current state of the field. We cover what computer vision is, how it works, and how it’s being used across industries. You’ll discover:
- Key capabilities of modern computer vision systems
- Real-world applications in manufacturing, healthcare, retail, logistics, and more
- Emerging trends, such as visual general intelligence and spatial AI
To learn more about practical implementations and case studies, download our Computer Vision eBook.
What is Computer Vision?
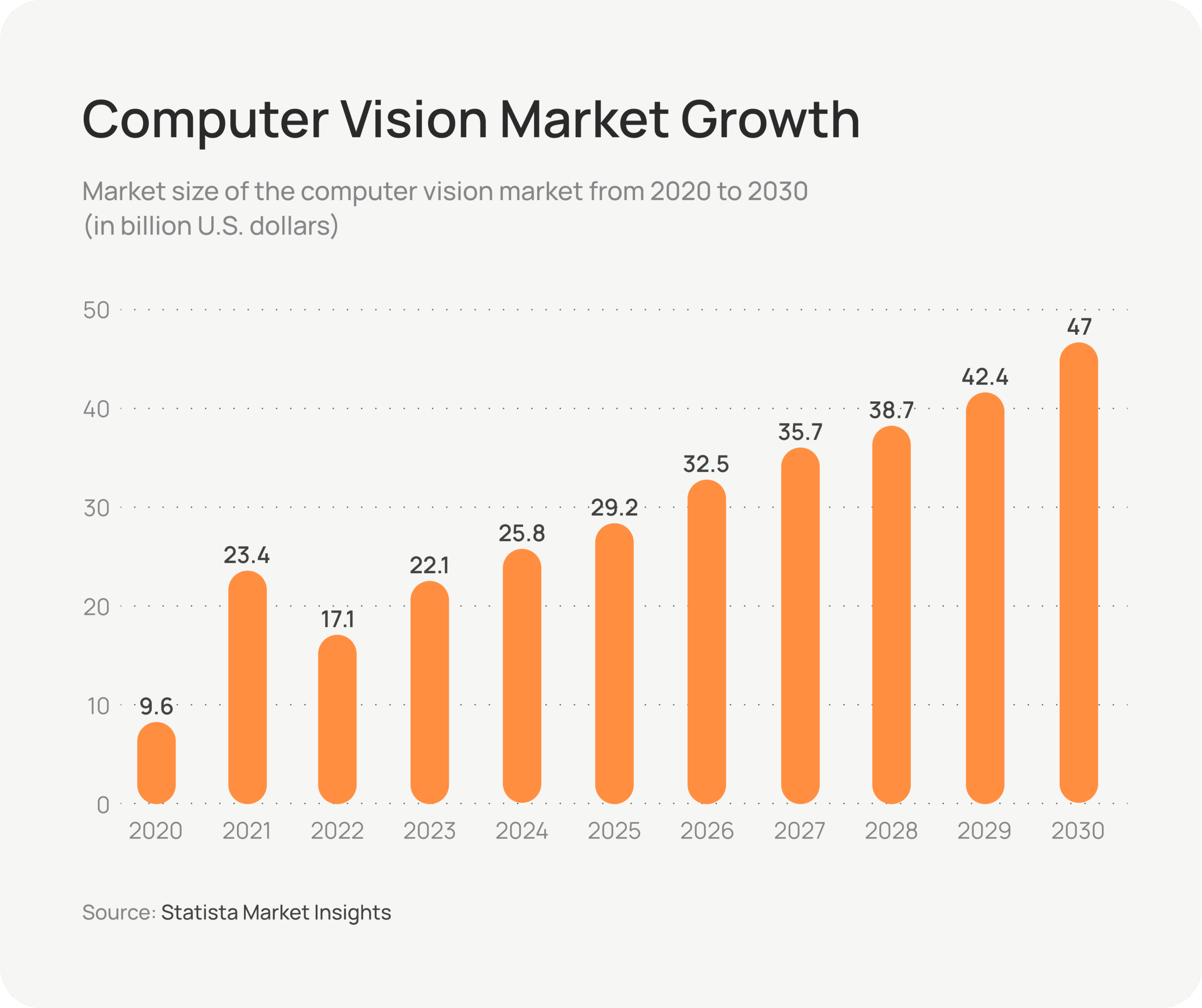
Vision used to require eyes. Now, however, it requires pixels, processors, and training data, and it’s faster than anything biological. Once confined to research laboratories, computer vision (CV) has become a practical, high-impact technology driving a market projected to grow from $25.8 billion in 2024 to $47 billion by 2030.
At its core, computer vision is a branch of AI that teaches machines to interpret visual data from images and videos. It works much like the human eye and brain work together to understand the world. This allows machines to recognize faces, read text, detect objects, measure distances, analyze movements, and spot patterns in real time.
Computer Vision Capabilities
Over the years, computer vision has evolved from basic algorithms to modern, AI-driven methods that redefine the possibilities of image analysis. Its main capabilities include:
- Image classification identifies what is in a picture.
- Object detection pinpoints multiple items within a single frame.
- Semantic segmentation analyzes images pixel by pixel to define object boundaries.
- SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) allows robots and autonomous vehicles to navigate unfamiliar spaces in real time.
Understanding the Role of Computer Vision in Business
Some business tasks are too large or complex for humans to manage effectively. In manufacturing, for example, workers cannot manually inspect thousands of products on a production line without making mistakes. In security and surveillance, it is hard for people to monitor many cameras at once. In healthcare, radiologists struggle to spot subtle issues in medical scans. Even in robotics and assembly lines, hidden misalignments or deformities in complex 3D parts can be overlooked. Computer vision helps with these problems by continuously analyzing visual data on a large scale. It highlights important issues in real time and allows businesses to maintain quality, safety, and efficiency across different industries.
Studies and real-world applications show computer vision in action. McKinsey finds that AI-powered quality inspection can cut costs by as much as 50% and improve defect detection rates by up to 90%. Accenture reports that 71% of retailers are investing in CV for inventory management and customer experience. The GenAI4Q system at BMW’s Regensburg plant uses computer vision and real-time production data to automatically create inspection plans for the 1,400 vehicles built each day. This improves quality control and ensures consistent premium standards across thousands of unique configurations.
Explore Computer Vision Use Cases
The growth of Industry 4.0 and smart automation has boosted the need for computer vision in various sectors. The computer vision trends of 2025 show this growth, with applications already found in manufacturing, retail, healthcare, logistics, agriculture, transportation, and more.
| Industry / Sector | How CV is Applied | Example Impact |
| Manufacturing & Quality Control | Detects faulty products before shipping, monitors equipment to prevent failures | Detects faulty products before shipping, monitors equipment to prevent failures |
| Healthcare | Analyzing medical scans, endoscopy lesion detection | Helps doctors catch precancerous conditions earlier and more accurately |
| Retail & E-Commerce | Smarter listings, better visual presentation, improved inventory accuracy, enhanced product identification and seamless in-store navigation | Smarter listings, better visual presentation, improved inventory accuracy, enhanced product identification and seamless in-store navigation |
| Logistics & Warehousing | Package inspection, inventory tracking, autonomous vehicles | Streamlined operations, faster deliveries, reduced errors |
Agriculture | Drone-based crop monitoring, plant health analysis | Optimizes yield, detects crop issues early |
| Transportation & Airports | Facial recognition, object detection in autonomous vehicles | Faster identity verification, improved safety, pedestrian and vehicle detection |
| Security & Surveillance | Intelligent CCTV, anomaly detection | Detects unusual activity in real time, enhances safety |
| Content Moderation & Online Platforms | Automated image and video analysis | Ensures safe and clean digital experiences |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Drone inspection of buildings, bridges, and job sites | Reaches hard-to-access areas safely, identifies structural issues early |
| Insurance & Automotive | Visual claims analysis, damage assessment | Speeds up claims processing, improves accuracy |
| Augmented Reality / Tech | Surface and object recognition for overlays | Enhances AR experiences, supports interactive applications |
In our Computer Vision eBook, we explore how organizations use computer vision to innovate and transform their everyday operations and tackle complex challenges. Fill out the form to download our eBook “State of Computer Vision in 2025” and learn about specific real-world use cases for computer vision across industries.
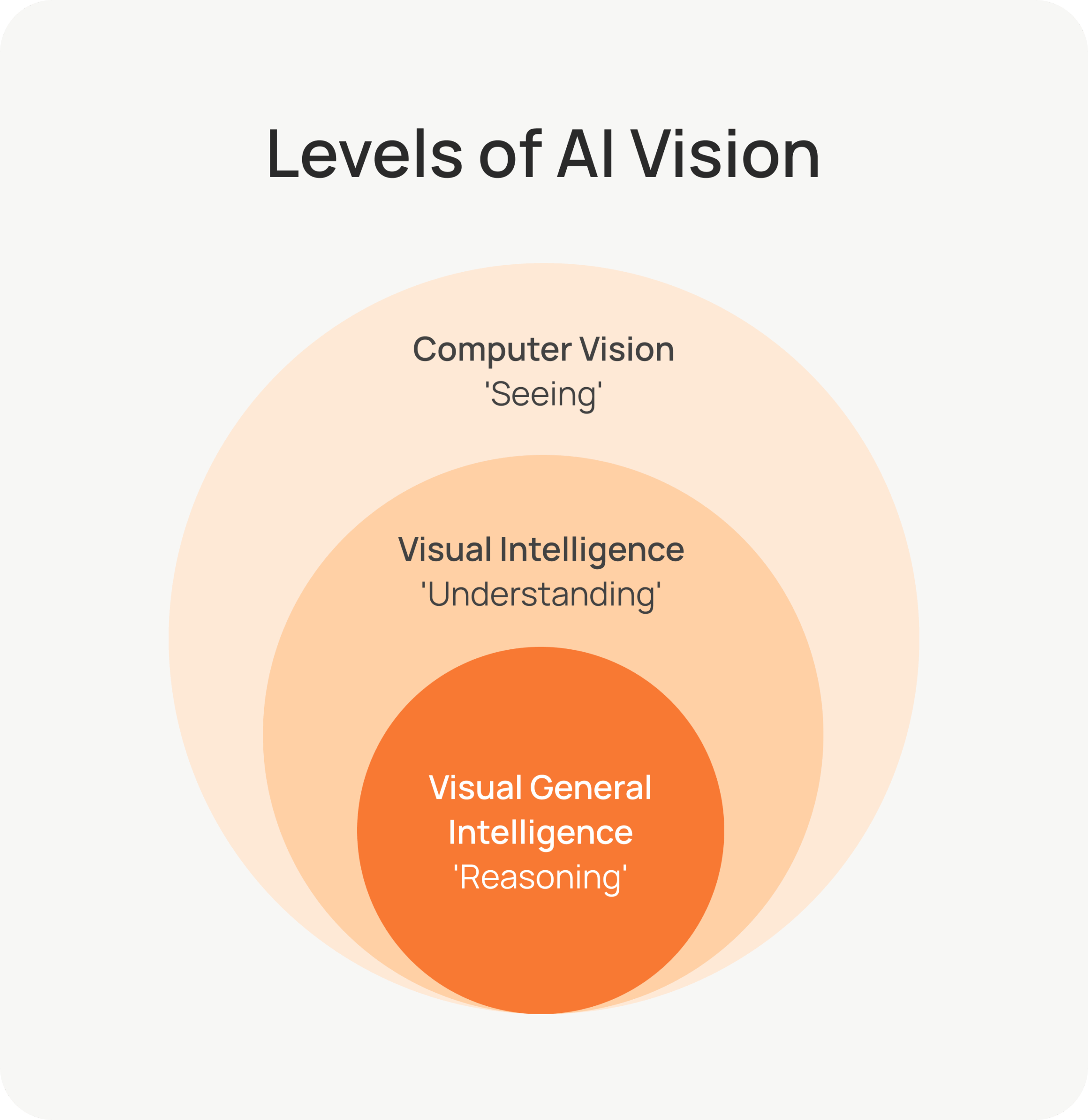
Future of Computer Vision
We are heading toward a future where visual general intelligence (VGI) is possible. Computer vision, once a narrow, task-specific tool, is changing into general-purpose intelligence that can see, reason, and act in the physical world.
In this next stage, models will understand and reason about any visual input. They will adapt across different tasks and fields without needing retraining. Like human vision, VGI will process information based on clear goals and desired outcomes, blending perception, language, and action in a flexible, human-like manner.
Thus, computer vision is moving from passively analyzing visuals to actively interpreting relationships, predicting changes, understanding context, and interacting with visual environments similarly to how humans do.
The real computer vision breakthrough lies in vision-language models (VLMs) and their successors. VLMs learn from image-text pairs to create a rich understanding of the world that combines different types of information. This enables machines to interpret visuals in context and respond using language. For example, you might ask a VLM: “Compare these six images and estimate the distance between the dog and the fire hydrant.”
Emerging Computer Vision Trends of 2025 and Beyond
The latest developments in computer vision in 2025 show applications expanding into new areas that combine perception and action.
Robotics
Robotic perception is evolving into a new frontier at the intersection of vision, reinforcement learning, and simulation. This shift toward spatial AI enables systems to not only see and classify, but also to understand relationships, motion, and causality. Instead of relying solely on cameras, modern systems combine multiple sensor inputs, semantics, geometry, and reasoning to interpret complex scenes in real time.Researchers aim to give robots an intuitive sense of the world — not just the ability to recognize objects, but also the ability to reason about how they can move, interact, or be manipulated. As Luca Carlone, an associate professor in MIT’s Department of AeroAstro, puts it:
“Perception is a big bottleneck toward getting robots to help us in the real world. If we can add elements of cognition and reasoning to robot perception, I believe they can do a lot of good.”
The shift is supported by a thriving open source ecosystem (MIT alone has released 60+ repositories), accelerating progress in perception, scene understanding, and robot reasoning.
Self-driving cars
Self-driving cars are among the most advanced and visible applications of computer vision. These systems use a combination of cameras, LiDAR, radar, and GPS to perceive their surroundings, recognizing lanes, traffic signals, pedestrians, and other vehicles in real time. The long-term goal is for autonomous vehicles to primarily navigate by sight, much like human drivers do, by interpreting complex and constantly changing environments through visual reasoning.
“Soon, everything that moves will be robotic, and the car is the next one.” – Jensen Huang, NVIDIA founder and CEO.
To achieve this, vehicles must fully understand their surroundings — identifying what’s around them, how far it is, and how it’s moving. Powered by 3D vision and spatial AI, they use stereo cameras and point clouds to perceive depth and motion. Combined with reinforcement learning and simulation, these capabilities enable cars to anticipate changes and make safe, real-time driving decisions.
AI models are now trained on millions of real-world driving scenarios, which enhances their ability to react to diverse and unexpected situations.
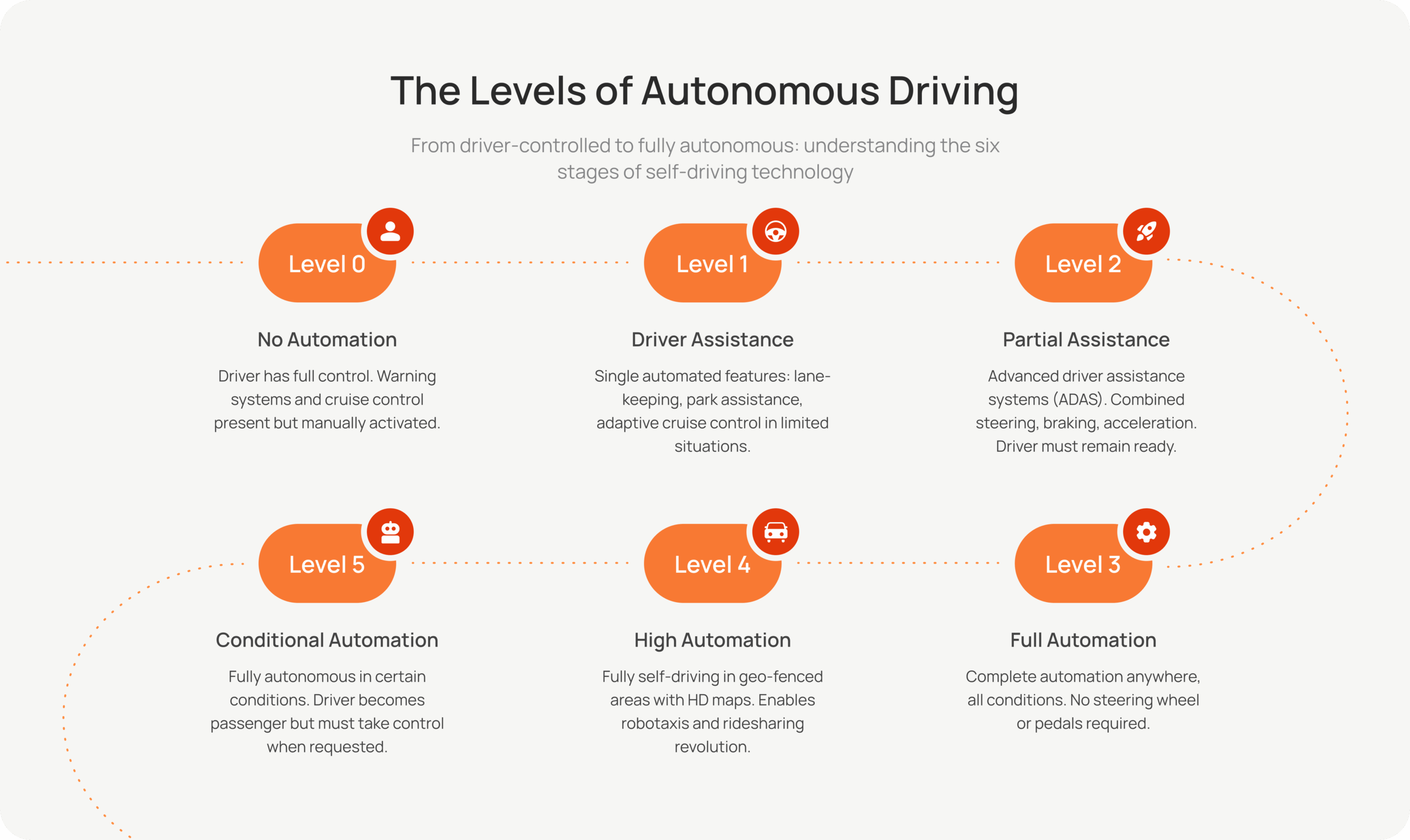
Currently, most vehicles operate at Level 2 autonomy, providing assistance with steering and speed. However, manufacturers like Mercedes-Benz have achieved Level 3 autonomy, enabling limited hands-free driving under specific conditions. The industry’s ultimate goal is to achieve Level 5 autonomy, which would mean having fully self-driving vehicles that can operate anywhere without human intervention. This will require AI that can reason in real time, adapt to changing environments, and ensure absolute safety in all driving conditions.
Enterprise Computer Vision Deployment
Building a computer vision model is only half the battle. The real challenge begins when you try to get it to work reliably in a production environment. Transforming a research prototype into a product involves addressing deployment complexities, hardware constraints, and performance tuning.
To understand how these challenges translate into real-world costs, check out our Computer Vision Price Guide Every Business Needs. It explains what drives project budgets and shows where investments provide the most value.
If you’re planning a CV-powered MVP or exploring how to bring your model to production, download our eBook to discover practical insights, real-world use cases, and the technologies driving the next generation of computer vision systems.