The coronavirus pandemic has exposed weak points and failures in the worldwide healthcare system.
The number of patients affected by the virus is escalating dramatically each day, while shortages in supplies and professionals raise fears that not everyone that needs treatment will get it. Furthermore, social distancing and quarantine measures are forcing many doctors to cancel routine and non-emergency appointments.
As this article is being written, there are already 790 thousand people worldwide affected by COVID-19 and this number will probably be much larger by the time you read it.
Is there any chance this number could have been less or at least have grown slower? We bet the use of modern technologies and the digitalization of the healthcare vertical might be the real solution, especially the use of Telehealth.
Telehealth keeps you home and healthy
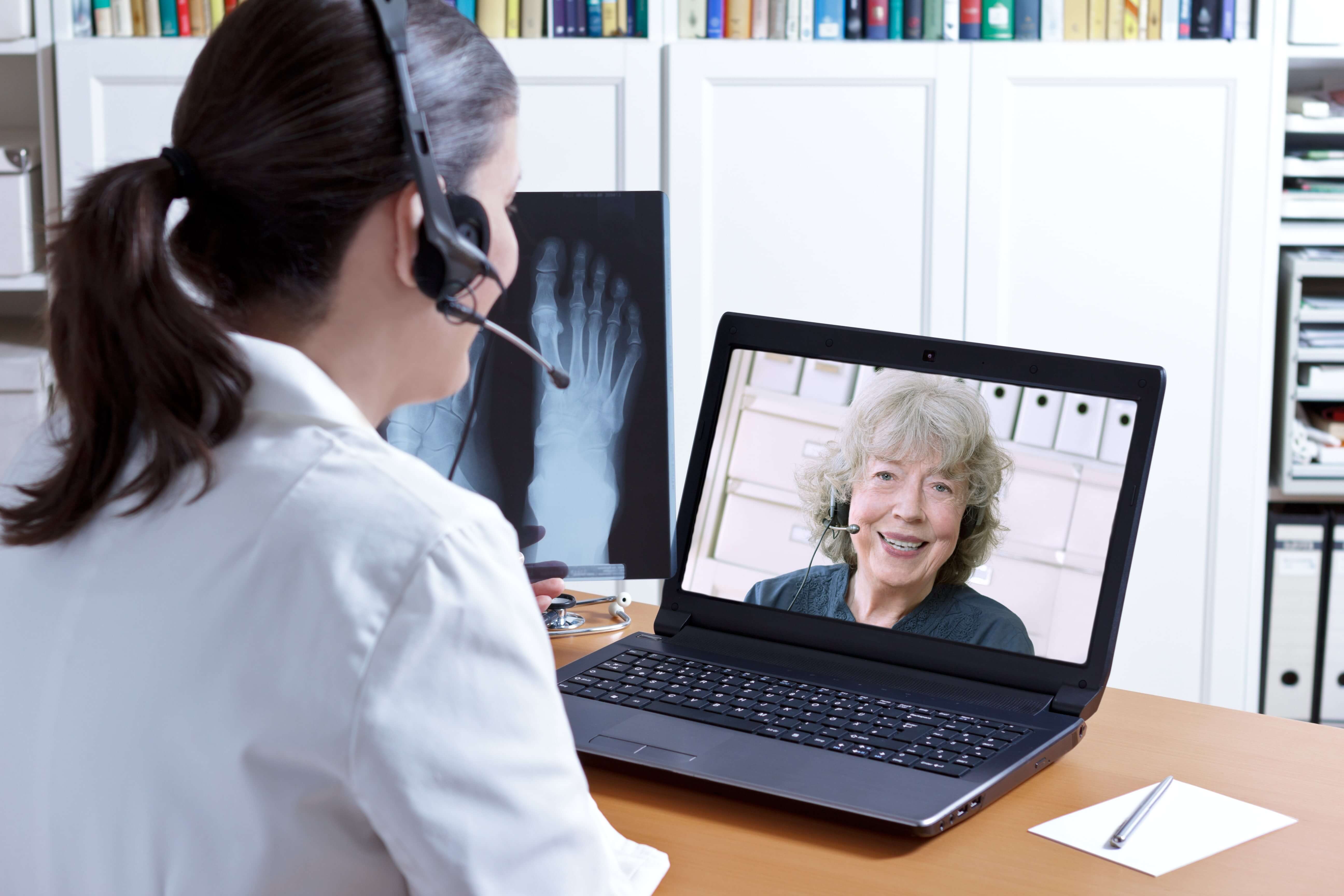

Telehealth is the access and distribution of health-related services via various telecommunication tools. For example, the use of mobile technology for live video doctor consultations or remote patient monitoring. Such tools extend the reach of physicians and healthcare providers beyond traditional clinical settings. Telehealth enables a constant relationship between patients and caregivers and offers providers a continuous stream of real-time patient health data.
Telehealth reduces the physical strain by minimizing in-person visits for non-emergency patients, freeing up time in triage, and creating more space for serious and urgent illnesses.
These digital tools also grant hospitals and clinics a broader reach, help to augment decision-making, deliver more personalized care, and improve patient engagement and loyalty.
Here are the most recognizable subcategories of telehealth:
Telemedicine — the most common subset of telehealth. It refers specifically to clinical services provided using telecommunications technology, like a phone call, video chat, or text message.
Telemonitoring — or remote patient monitoring, is a method to monitor patient health data outside of clinical settings via modern technologies and wearables. Telemonitoring refers to the specific technologies used to electronically transmit information between patients and physicians.
Telenursing — allows nurses to interact with patients and monitor their conditions through mobile devices and complex computer-based systems that utilize video and audio features integrated with medical monitoring systems, as well as remote patient monitoring tools. Thanks to that, nurses can provide immediate, ongoing care, and can better consult their patients leading to improved clinical and health service outcomes regardless of geographical location or distance.
Hospital chatbots — like ordinary ones, they are computer programs or smart algorithms conducting conversation via auditory or textual methods. They are learning from thousands of interactions in order to increase the accuracy of patients’ disease recognition. Hospital chatbots are helping patients with symptom-based diagnosis, give instant feedback regarding general health questions, and help to distinguish urgent cases from low-emergency ones which help hospital workers a lot.
Everything said above is neither rumors nor fantasies, for example, East Boston clinic, which serves about 300,000 patients annually, has performed over 1,200 telehealth audio visits in just a few days after the pandemic outbreak in the USA.
Some healthcare platforms already provide telehealth solutions for hospitals, doctors, and patients. Since it is an omnichannel platform, it provides multiple tools from live-video doctors’ appointments, patient monitoring, EHR management, medical chatbots to even AI-based diet optimization based on a biochemical blood test.
With the platform’s chatbot designer, it is possible to configure various communication scripts with patients to distinguish cases into needed categories, for example, emergency, non-emergency, COVID-19, or others.
In addition, patients can learn how to behave in different situations, as well as provide doctors with survey responses to the results of their treatment.
AI diagnostics and decision-making
Predictive analytics uses AI and statistical methods to search through massive amounts of historical data, analyzing it to estimate the likelihood of outcomes for individual patients. Predictions can range from responses to medications, the need for surgeries, to hospital readmission rates.
Predictive diagnostics is based on lab testing, biometric data, claims data, patient-generated health data, and the social determinants of health.
Since early diagnosis is very crucial for patient care, AI is being used to cut down the time it takes to diagnose serious illnesses. The way AI rapidly processes large amounts of information and arrives at likely causes for symptoms can drastically reduce the diagnosis-treatment-recovery cycle for many patients. These benefits are clearly seen in the realms of intensive care, surgery, or emergency care, where a patient’s life might depend on quick reaction time.
Smart diagnostic systems are able to screen chest X-rays in a matter of seconds to detect different pathologies with an accuracy rivaling that of radiologists.
These systems can help with the diagnosis of urgent care or emergency patients who come in with, for example, cough and differentiate pneumonia caused by the coronavirus from pneumonia caused by the “swine flu” strain.
Instead of conducting tissue-destructive tests or relying on genomics, AI algorithms can harness information from images to identify patients with a more aggressive disease who are therefore in need of more aggressive treatment. It could also let physicians know which patients have less aggressive cancer and might be able to avoid the side effects of chemotherapy. For example, Baidu Research claimed that its breast cancer detection algorithm can outperform human pathologists in breast cancer metastasis identification based on early tests.
AI assists physicians and health professionals with clinical decision-making tasks.
Another side of AI implementation is clinical decision support systems (CDSS), which are designed to provide physicians and other health professionals with clinical decision support, i. e. assistance with clinical decision-making tasks. These systems generate case-specific advice based on Big Data and a particular patient’s data.
Microsoft’s Hanover project analyzes medical research to predict the most effective cancer drug treatment options for patients. First Databank’s clinical decision support technology specializes in installations of e-prescribing, EHR, EMAR, and CPOE systems and prioritizes delivering concise, immediate electronic messages to physicians offering up-to-date drug information for active clinical decision support.
Paracelsus uses a large set of modules with Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Neural Networks to support all processes in hospitals from EHR management to the creation and management of treatment scenarios. The system analyzes patients’ data and makes predictions on the need for surgeries, types of prescribed medicine, patient hospitalizations, and more.
VR and AR enhancements
AR and VR technologies already offer serious promises for the healthcare industry. From students educating and patients rehabilitation to performing procedures and surgeries. Medical professionals are using AR and VR-enabled devices for cheaper and more accessible technology to diagnose, treat, as well as cure advanced illnesses, and much more.
AR and VR are helping to retrieve memories for those who suffer Alzheimer’s and ease concerns ranging from dementia to cognitive impairments.
Enhanced and simulated environments enable more diverse interactions that might otherwise be possible during physical therapy, i. e. returning them to a time, experience, or sound that was important to them in the past. Data is gathered via monitoring and assists therapists in delivering customized care plans.
For example, Maplewood Senior Living is already utilizing VR headsets to create special environments for patients and unlock their memories, improving their emotional well-being.
VR is also helpful in treating peoples’ phobias. For instance, phobia of height can be almost fully treated using VR activities.
And one of the most vital benefits, for now, is that VR has revolutionized the way surgeons are being trained by bringing a “real” hands-on experience for them.
Medical students can watch live operations via VR helmets in detail without the struggles of catching the glimpse of the process. And the locations don’t matter anymore — surgeons from different parts of the world can be a part of any important operation. They can move around and communicate as if they were present in the operating room.
More sustainable care

While implementing Telehealth into hospitals and delivering medical care via the internet brings us more personalization and comfort, it also means you need to go to a hospital less. And this the exact reason Telehealth dramatically reduces medical wastes from various tests and protective gear.
Because today all the garbage contaminated with bodily fluids or other infectious materials is quite a big concern for hospitals, especially with escalating numbers of patients sick with COVID-19.
To examine any patient with a possible coronavirus infection, health care workers have to go through medical supplies and disposable personal protective equipment every time. Eventually, all that used gear piles up as medical waste that needs to be safely discarded.
In Wuhan, officials had not just to build new hospitals, but also to construct a new medical waste plant and deploy 46 mobile waste treatment facilities too.
At the peak of the outbreak, hospitals were generating six times more medical waste than before the beginning of the crisis.
The daily waste output was around 240 metric tons which is about the weight of an adult blue whale.
Conclusion

The future of our healthcare system should be about the collaboration of technologies and healthcare institutions to make good medical care accessible and affordable to people from all walks of life. The coronavirus is damaging the world economy and costing thousands of lives, which shouldn’t be in vain. Because the coronavirus pandemic is just one of the numerous issues we are facing now and will be in the future. The enhanced and renovated healthcare systems can lower or even totally reduce numbers of future victims of various illnesses.
So if you have the urge to move digital during these challenging times, feel free to drop us a line. Our healthcare software consultants will get back you as soon as possible and gladly assist you with your custom software development.