The healthcare sector has undergone a major transformation in recent years, moving from a focus on volume-based care to value-based care. As a result, there is a growing demand for creative solutions that enhance access to healthcare for all patient groups, regardless of factors such as transportation difficulties, a shortage of healthcare providers, geographical barriers, or financial constraints. These solutions aim to ensure that quality and efficient healthcare is readily available to everyone.
- What Is Remote Patient Monitoring?
- Why is it important?
- Remote Patient Monitoring is set to expand rapidly
- RPM Market Statistics
- How does remote patient monitoring work?
- Technology driving RPM devices
- Common remote patient monitoring devices
- Best practices for PRM
- Bringing RPM to Life with Softarex’s Expertise
What Is Remote Patient Monitoring?
Often abbreviated as RPM (and sometimes known as remote patient management), remote patient monitoring is a method of healthcare delivery that uses the latest advances in information technology to gather patient data outside of traditional healthcare settings. Remote patient monitoring refers to the use of a specific technology to facilitate interaction between clinicians and patients at home.
Why is it important?
Remote patient monitoring is a virtual technology that enables healthcare providers to gather and analyze medical and health data from patients for assessment, recommendations, and instructions. This information, which can include vital signs such as blood pressure, weight, heart rate, and blood sugar levels, can be captured electronically without the need for an in-person visit to a medical practice. With RPM, patients can receive healthcare services from the comfort of their own home, office, vacation spot, skilled nursing facility, or any other location as long as they are not in a shared space with the healthcare provider delivering the services. Thus, RPM is a revolution in healthcare delivery that provides a multitude of benefits for patients, healthcare providers, caregivers, and the entire healthcare system.
Wide ranging benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
- Improves data driven clinical decision making
- Helps patients improve self management and care plan adherence
- Cost of Care reduction for payers and providers
- Boosts net patient revenue
- Improves patient outcomes
- Reduces patient’s expenses and improves work productivity
- Improves access to care
- Builds patient engagement
- Optimizes clinical staff efficiency and combats clinical staff shortages
- Prevents the spread of infectious diseases and Hospital-Acquired Infections
- Boosts caregiver connectivity and involvement in care
- Improves patient experience and satisfaction
- Expands referral opportunities and improves retention
- Improves the clinician-patient relationship
Remote Patient Monitoring is set to expand rapidly
The results of a survey of large healthcare facilities on their opinions about the current state of remote patient monitoring reveal substantial progress and advancement of RPM technology during the COVID-19 pandemic and predict its rapid growth in the next five years. An increasing number of healthcare providers are recognizing the advantages of RPM technology and its related services.
According to the survey, 43% of the respondents believe that the use of remote patient monitoring will be on equal footing with in-patient monitoring in five years, while 35% anticipate it to surpass in-patient monitoring within that time frame. 20% of the participants reported already implementing RPM, while another 23% plan to do so within the next 12 months. With regards to the collection of remote data, 90% of the respondents deemed continuous 24-hour data to be more valuable than episodic data.
RPM Market Statistics
The statistics, facts, and figures presented below clearly highlight the potential for remote patient monitoring to become a significant aspect of healthcare delivery in the future. This is because RPM is not only highly profitable for medical practices, but it is also widely accepted by both patients and payers. The popularity of virtual care and telehealth also supports this trend.
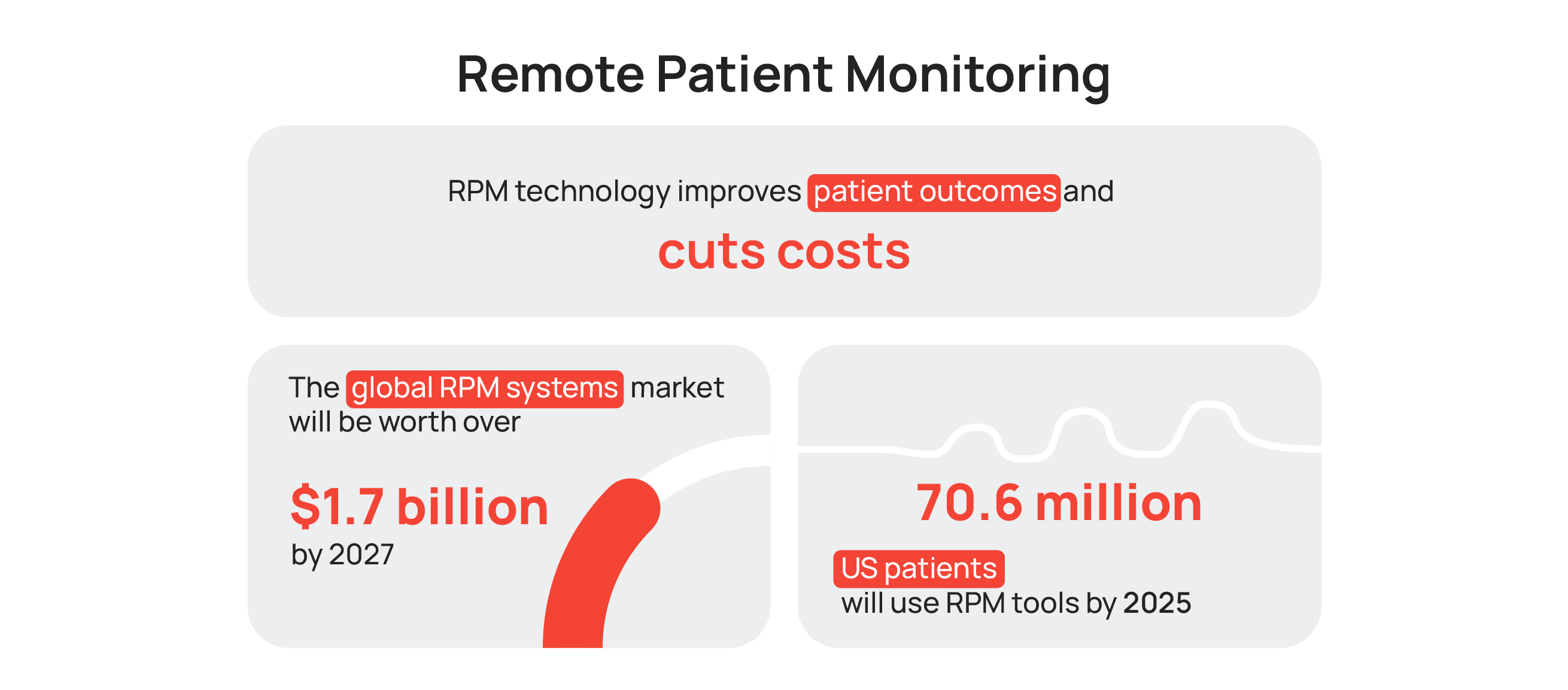
The projection for the use of RPM tools in the US is that by 2025, 70.6 million patients, equivalent to 26.2% of the US population, will adopt the technology. Healthcare providers who have adopted RPM-powered home health monitoring systems and telehealth services have already observed a decrease in hospital readmission penalties. For instance, the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center reduced the risk of hospital readmissions by 76% while maintaining patient satisfaction rates over 90% by providing patients with RPM equipment and tablets.
Seniors are particularly benefiting from RPM technology and home-based care, largely due to their high prevalence of multiple chronic diseases. A KLAS Research report, which analyzed 25 healthcare organizations, revealed that 38% of healthcare organizations implementing RPM programs for chronic care management reported reduced hospital admissions and 17% reported cost savings.
How does remote patient monitoring work?
Having outlined the definition of RPM, it’s time to delve deeper into the service. So, what exactly is remote patient monitoring and how does it work?
Step 1. A healthcare provider determines which health conditions can be managed remotely and establishes a remote patient monitoring program to offer RPM services to patients. Through this program, the provider can collect a wide range of patient health data, including:
- blood pressure
- heart rate
- vital signs
- weight
- body temperature
- blood sugar levels
- breathing patterns
- SpO2
- CO2
Step 2. A healthcare provider determines that a patient would benefit from remote monitoring of certain physiological parameters and, with the patient’s consent, initiates the process of ordering or prescribing RPM. This enables a provider to capture and track relevant health data through remote patient monitoring.
Step 3. The patient is provided with a device to collect the health data. The device must be electronically connected for remote patient monitoring, which is typically achieved through cellular networks or Bluetooth connectivity.
Cellular remote patient monitoring devices collect and transmit patient health data over the same networks used by our cellphones. In contrast, those RPM devices that use Bluetooth technology transmit patient data through short-range wireless connections to devices that have internet connection.
Step 4. Once the remote monitoring device has been properly configured, it collects and transmits health data from patient to provider, typically via electronic means. Sharing this information with healthcare providers facilitates efficient diagnoses, treatments and disease management procedures, which in turn can be assessed and relayed to patient management systems and shared with insurers and relevant healthcare organizations.
Step 5. The provider analyzes this data and gives the patient health and wellness guidance and directions based upon the results.
Technology driving RPM devices
PRM services require technology that collects and interprets physiologic data. In a typical remote health monitoring setup, the following key technology components are used:
- Body wearable (IoT) sensors
- A handheld computing gadget (mobile phone or a tablet computer) with a patient app installed on it
- Remotely located (cloud-based) application server accessible through internet (mobile or Wi-Fi) communication
- Hospital side software
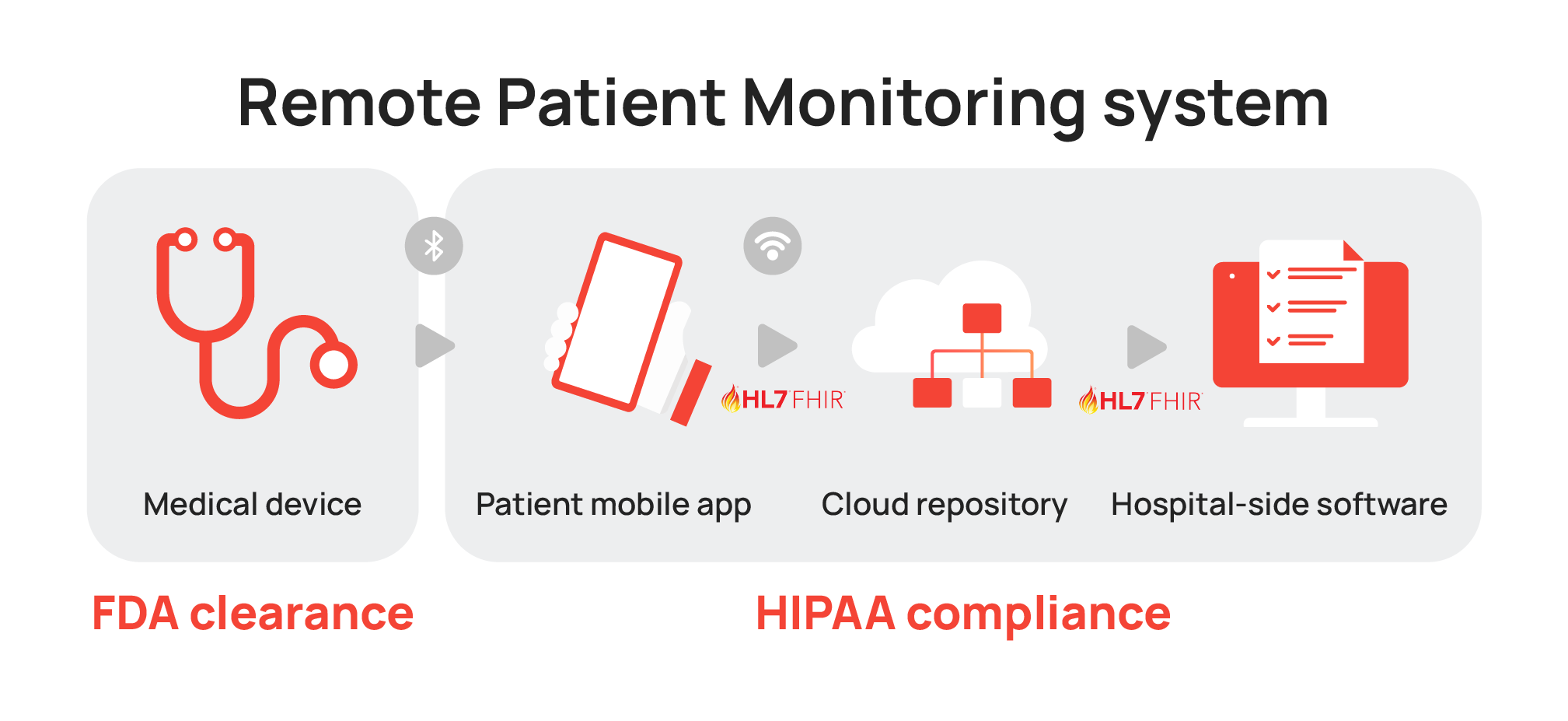
These wearable sensors gather data on human body parameters and send it to the remotely located server for evaluation and analysis by medical experts, who, in turn, determine its level of criticality and then take appropriate action.
Common remote patient monitoring devices
There is a wide selection of remote patient monitoring devices available on today’s market. A majority of these devices are well-known to patients.
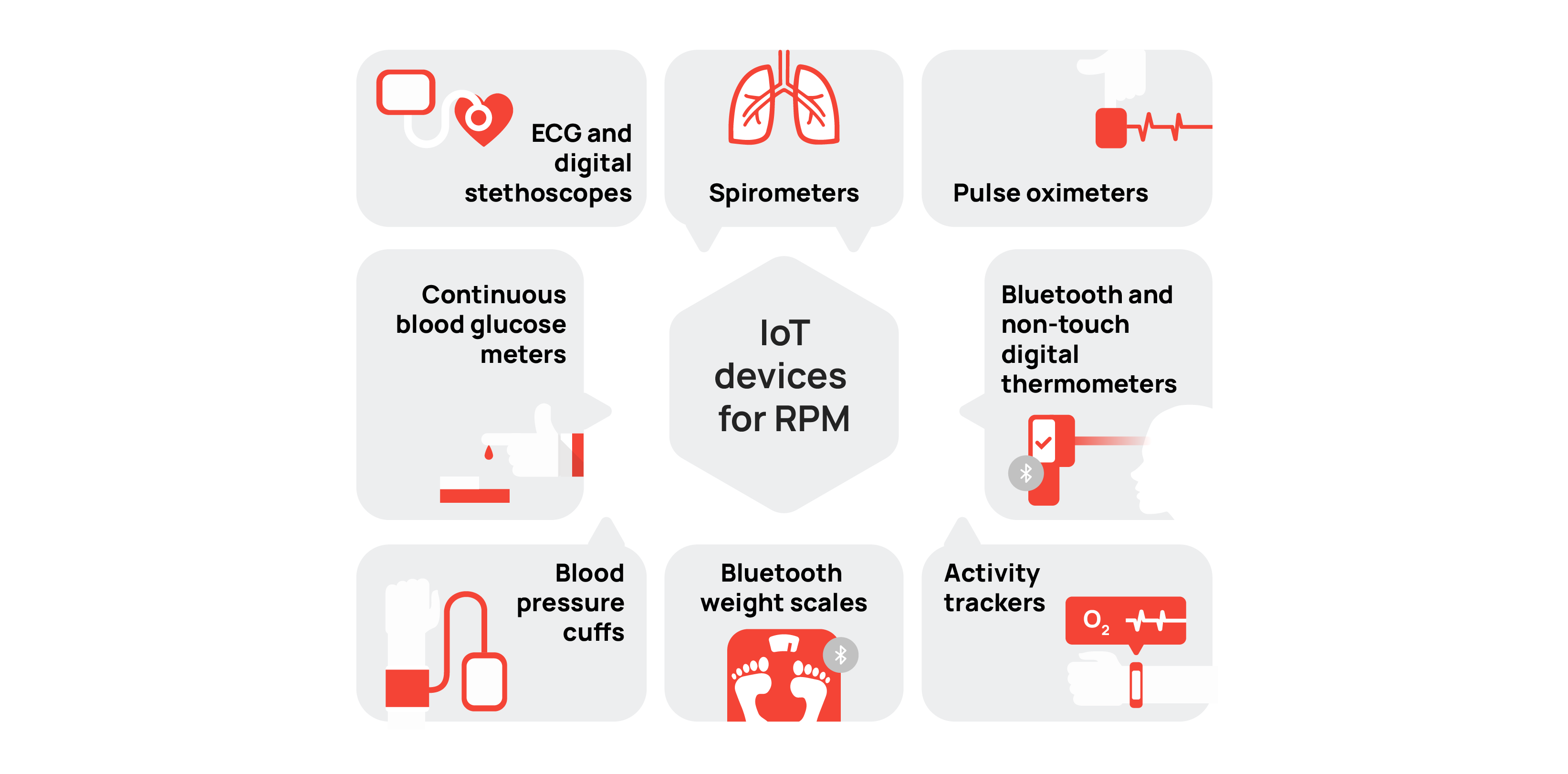
Blood pressure cuffs calculate a patient’s heart rate and blood flow by measuring changes in artery motion. The Bluetooth version of this device instantly gathers data on heart rate and blood pressure. All that data goes directly to practitioners and doctors for review.
Bluetooth weight scales allow patients to track changes in their weight over time,
and the provider to keep an eye on these changes to prevent the worsening of symptoms on time.
Continuous blood glucose meters test a patient’s blood sugar through a small drop of blood placed on a test strip that is connected to the device. When a patient uses a blood glucose monitoring device, the information is collected at a specific time and sent directly to practitioners.
Digital glucometers help avoid the life-threatening condition of ketoacidosis. Bluetooth and non-touch digital thermometers provide a fast and accurate picture into the patient’s body temperature.
Spirometers are used for pulmonary function testing and diagnosing lung conditions such as asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
Activity trackers assist in maintaining an active lifestyle by monitoring a patient’s physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns.
Pulse oximeters are wearable SpO2 monitors that provide continuous tracking of a patient’s oxygen saturation levels. Pulse oximeters are used to determine blood oxygen level for COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), CHF (congestive heart failure), or in COVID-19 patients.
ECG monitors capture heart function, while digital stethoscopes capture heart and lung sounds. The ECG is commonly used for patients with cardiac conditions like arrhythmias or coronary artery disease.
Beyond traditional monitoring devices, innovative diagnostic technologies are improving the effectiveness of remote patient monitoring. Advanced reflex diagnostic systems can now carry out thorough health assessments in just 15–20 minutes, identifying potential pathologies earlier than conventional methods can. Read our case study on the Automatic Reflex Diagnostics System to learn how integrating cutting-edge diagnostic hardware with intelligent software processing is transforming patient evaluation and the early detection of diseases.
Best practices for PRM
There are certain aspects you should consider before starting the development process for the remote patient monitoring system.
Patient friendly experience
The primary users of any PRM system are elderly people and patients, followed by doctors and physicians. That is why it is important to make the design and user experience as patient friendly as possible. Make sure that the solution is inclusive, and incorporate accessibility features, such as, for example, voice-guided control for patients with motor dysfunctions and vision impairment, or text-to-speech functionality for visually impaired people.
Data analytics and reporting
Business intelligence and data visualization tools in remote monitoring applications are highly valued by healthcare providers. Doctors need these tools to effectively analyze patient health data and make informed decisions.
Speaking of data-driven healthcare solutions, our experience extends beyond traditional RPM to innovative nutrition management systems. Related: Personalized Diet Plans Generation System.
Battery optimization
To ensure reliable and consistent data for patients, a remote patient monitoring application must conserve battery life while constantly monitoring physical conditions. This can be achieved by limiting background processes, incorporating a battery-saving mode, and providing notifications for data transmission interruptions.
Offline access
The remote patient monitoring platform should be able to handle internet connectivity outages. Secure constant monitoring of vital patient information by implementing caching mechanisms and local notifications.
Geolocation and Voice search features
Features like geolocation and voice recognition can make patient monitoring apps more effective. A geolocation feature can help home health patients find the nearest clinics or pharmacies in emergencies, and voice search function makes it easier for senior patients to access care services.
Ensure IoT Data Security with Encryption
Embedded devices currently use asymmetric lightweight cryptography (LWCRYPT) techniques, which involve incorporating key encryption into the wearable sensors. This helps establish protected data transfer channels, ensuring the privacy and security of sensitive information transmitted through the IoT devices.
Patient data security and compliances
To secure information access, implement complex authentication and establish clear policies on who can access the data and under what conditions.
It is also important to ensure that the application is compliant with relevant regulations, such as HL7, HIPAA, and HFIR, and gets an FDA clearance. If the application is connected to wearable devices like sensors or trackers, it should also comply with IEC 62304 safety standard.
Bringing RPM to Life with Softarex’s Expertise
Remote patient monitoring is rapidly gaining popularity among patients and healthcare practices. With its increasing demand, it is essential for healthcare practices to consider incorporating RPM into their services.
With over 15 years of experience in developing systems for the healthcare sector, Softarex is ready to offer their expertise and help you bring your best healthcare solution to life.









