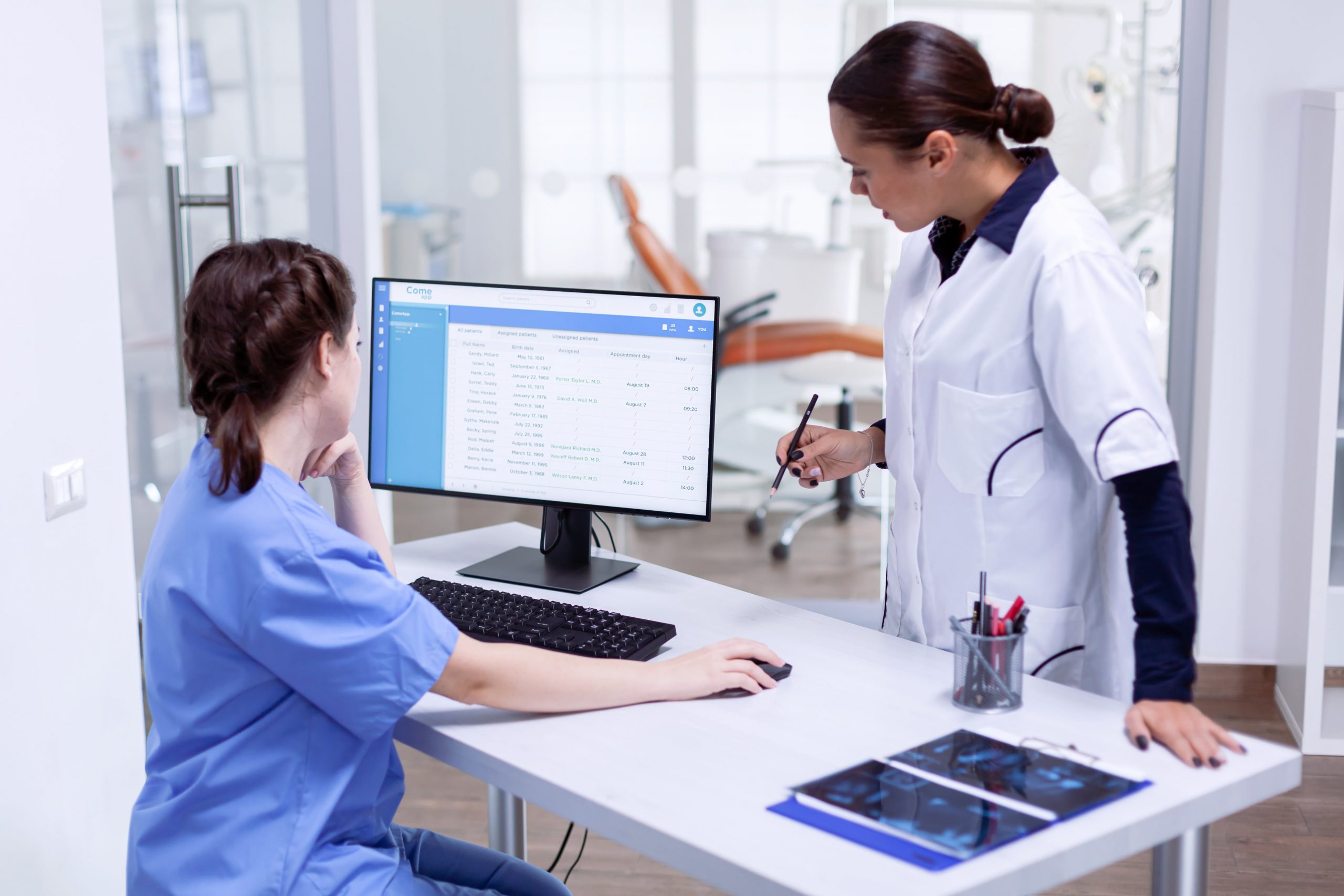
While we were reviewing Telehealth and its subspecialties such as Teleradiology and Teledermatology, we often mentioned Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. We think it’s time to look at them more in detail.
You’re probably already familiar with EHR in some way, perhaps even your hospital has a similar system installed. The current problem with these systems is that they are decentralized and run locally — on on-site servers.
Today, many SaaS platforms offer solutions that are much more convenient, functional, and intelligent in every way. But before we discuss all the advantages of the cloud option, let’s take a closer look at what EHR, EMR, and MPMS are.
Electronic Health Record

An electronic health record (EHR) is basically a digital version of a patient’s paper chart. Instead of a thick folder, EHR software can store all digital records and provide an overview of patient care. EHR solutions can do anything from keeping a patient history to integrating pharmacies and billing.
EHR can reduce the number of errors and legibility problems that occur with manual double entry and allow practitioners to see patients more quickly. This automation leads to more accurate diagnosis and overall treatment.
The EHR systems also have portals for patients to access their medical history and view medical records, giving patients more control in their overall treatment.
Medical Practice Management Software

Medical practice management software (MPMS), or just Practice management software (PMS), helps to handle all the daily work in a medical office. It bridges the gap between such clinical work as documenting diagnosis and procedure codes, planning patient visits, checking insurance, and managing medical billing tasks.
Although there are some features that may include patient information, MPMS is much more focused on office work. It is designed to manage patient flow and general documentation for a medical office as a whole, rather than for patient records or medical history. You still may find patient IDs in practice management but only with a little medical information. For example, MPMS may record patient demographics but usually does not include a patient’s medical history.
One critical component that seamlessly integrates with MPMS systems is automated appointment scheduling. Our recent work on a comprehensive Medical Scheduling System demonstrates how intelligent scheduling solutions can dramatically reduce administrative burden while improving patient satisfaction and reducing no-shows by up to 40%.
In addition to patient scheduling automation and billing, MPMS can process claims and generate reports. MPMS helps improve facility productivity and efficiency by allowing administrators and other staff to devote more attention and effort to patients rather than tedious and time-consuming documents.
Differences Between EHR, EMR, and MPMS

The main difference is that MPMS manages the day-to-day operations of an institution, EHR is a very patient-centric resource and they don’t overlap. Here we also have one more thing — Electronic medical records (EMR). EMR software, as well as EHR software, is related to documenting patient records. But unlike EHR, EMR is usually limited to a single clinic.
EHR and EMR
The terms EMR and EHR are often used interchangeably, but they are very different. EHR is a comprehensive digital compilation of a patient’s entire medical history, including medical history, doctor’s notes and data, medicines, patient hospital visits, diagnostic tests, etc., which are transmitted, managed, and stored in many different health settings.
The main difference between EHR and EMR is that EHR is constantly updated by health care providers and authorized personnel. EMR is a digital medical record of a patient’s medical history, but it is created, stored, and managed by only one provider. Generally speaking, EMR is used as part of patient diagnosis and treatment. EHR applications include more features and integrations than EMR, and thus require more investment to develop.
EHR and EMR have much in common, and both focus primarily on patient documentation as well as improved diagnosis and treatment. Recently, many healthcare insiders have started to use them interchangeably, so don’t worry if you mix them up — first of all, both systems lead to better treatment and diagnosis of patients.
EHR and MPMS
Both MPMS and EHR software rely on automation. MPMS automates tasks such as organizing meetings and planning specific tasks. With a practice guide, patient data such as names, demographics, insurance coverage, contact information, and more can be stored and reused. With EHR, health patterns can be recognized to detect allergies or even predict a diagnosis.
Instead of collecting all patient information every time you visit, you can do so at once and save it for later use. This saves time and effort associated with manual documentation and allows administrators to focus on more important tasks.
Another difference between EHR and MPMS is related to a particular user of the system. The receptionist doesn’t need to have access to detailed patient history, just as a doctor should have no reason to access patient health insurance information.
Office managers and support staff are the most common MPMS users, while doctors, dentists, and nurses are the main users of EHR. Although both are working to improve productivity, the use of EHR, in particular, allows medical facilities to speed up their visits and see more patients during the day. In addition, patients can access their medical history and make appointments through EHR.
Why should you choose Cloud over Physical server?

Web-based EHR solutions are becoming more popular and offer more benefits and flexibility compared to traditional, or on-premise, systems.
A web-based, or cloud-based, EHR solution does not use an internal server. In the cloud-based EHR systems, data is stored on external servers and can be accessed from any device that has an Internet connection, while on-site EHR systems store data on a personal server.
EHR cloud systems actually solve many problems that independent physicians may face with the local EHR system. With server-based EHR systems, thousands of dollars are often spent just to install and deploy servers, hardware, and software. In addition, regular maintenance and management by the on-site IT department are also necessary. In contrast, web-based EHR systems are already created as a service by a software vendor (SAAS), which means that the cost of money and time is drastically reduced.
Accessibility
When it comes to web-based EHR, accessibility is a key advantage. You can log in and work with your EHR wherever you are — the sole criterion is to have an Internet connection. This is especially important if the key physician is outside the facility and needs to review the patient’s medical history.
Similarly, the use of patient portals allows your clients to access laboratory results, communicate with their physicians, request repeat prescriptions, make payments, and much more. Patients can use the portal to provide basic information, which greatly reduces the number of forms they need to fill out manually. They can also receive reminders of prescriptions and tests that they need to perform, in addition to checking their patient records. This gives both doctors and patients more timely access to information.
Efficiency
Electronic prescribing is an excellent example of how to improve patient care, as it saves a lot of time for both patients and doctors. The benefits of e-prescribing are pretty obvious: doctors can quickly transfer new prescriptions to patients’ pharmacies, reducing redundancy, and minimizing the risk of errors. For example, pharmacists can be informed of any potential side effects of drugs or drug allergies that a patient may face. Patients also benefit because their prescriptions are often ready by the time they come to the pharmacy.
EHR helps speed up patient visits, which allows your healthcare organization to increase traffic and in turn increase income. Your healthcare professionals can pay more attention to patients and spend less time on spreadsheets and documentation. This allows doctors to treat more patients every day without sacrificing quality care.
Security
AJMC explained the main benefits of cloud-based EHR solutions: “In cloud systems, doctors don’t have to worry about system crashes, natural disasters, or weather conditions that can literally destroy systems in the blink of an eye. Backup requirements, protocols, and capabilities of traditional EHR/EMR systems are not always secure and do not provide guarantees. Patient data stored in the cloud will always be available, accessible from any location and at any time.
Security issues, especially with respect to patient confidentiality, are addressed through the careful and tactical efforts of the cloud server (such as risk analysis, data encryption, etc.) to ensure the safety and confidentiality of patient medical data. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has helped ensure and protect the confidentiality and security of medical information. This “health information” includes electronic patient health information (ePHI). Consequently, this type of data must be securely protected.
Smart Workflows
But above everything else, cloud-based solutions have much more extensions and additional tools that can be implemented into your cloud EHR system.
Using AI and Machine Learning, it is possible to create treatment scenarios, provide smart diet optimization based on biochemical blood tests, and analyze patient’s data to make predictions on the need for surgeries, medicines, hospitalizations, and so on.
Computer vision and AI algorithms can also help to triage cases in the system’s worklist so the most critical cases get the most immediate attention. AI algorithms can prioritize cases based on automated detection, for example, critical cases, such as the head CT with hemorrhage in the brain, are placed at the top and ordinary cases — at the bottom. In the long term, such a tool can combine interdisciplinary data with visual data to achieve the most reliable diagnosis, recommending further workup and prognosis.
In addition, many patients’ problems can be solved online. Meetings that do not require an office visit can be processed online and through mobile applications. To provide constant communication between doctors and patients, a cloud-based system can have chatbots with various communication scripts. Patients can learn how to behave in different situations, as well as provide doctors with feedback about the treatment results.
To sum-up

Cloud-based systems offer so many advantages over on-site server software that they just can’t be overlooked.
Cloud-based solutions are more powerful, more affordable, and much more intelligent. Also, you don’t need to update it manually or buy a new software version. It is updated as changes occur — automatically and overnight, so your workflow is virtually uninterrupted.
Additionally, cloud EHR makes it easier for multiple healthcare providers to work together. When a patient switches to a new provider or goes to another facility for specialized treatment, the new provider needs their information. EHR software allows you to easily share important information in real-time to ensure that the best possible care is provided to the patient.
If you consider installing an EHR, EMR, or MPMS system, we recommend that you look for a cloud-based one. If you have questions about which cloud-based solution to choose, or you are already using a cloud-based solution and facing any issues with it — feel free to reach us out. Our consultants will gladly answer all your questions and guide you with your custom software development.